Differences between Plant Stem Cell and Callus
Plant Stem Cell (CMC) and Callus (DDC) are Fundamentally Different Cells
Callus (A.K.A Dedifferentiated Cell, DDCs) is dedifferentiated tissue composed by a variety of heterogeneous cells from dozens of dedifferentiated cells obtained by dedifferentiation process on differentiated plant organs (such as leaves).
On the other hand, The CMCs developed by PIPSCI team are innately undifferentiated cells that has never been differentiated nor dedifferentiated, and CMCs are strictly homologous homogeneous cells.
Therefore, Plant stem cell (CMC) and callus (DDC) are fundamentally different from each other. Plant stem cell (CMC) and callus (DDC) show significant differences in cell morphology, gene expression, cell growth rate and stability, as well as plant active component synthesis due to their different origins.

| 
|
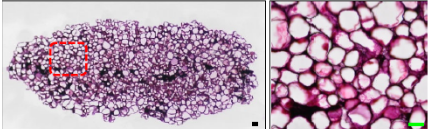
CMCs (left) • Thin-walled cells with similar cell size • Homogeneous cells • No damages during isolation process | DDCs (right) • Cells are very different in shape and size • Heterogeneous cells • Damages during isolation process |

 |  |
CMCs (left)
• Cells are arranged closely with uniform color, and separate from callus naturally • Composed of one type of cell |
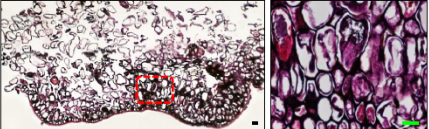
DDCs (right)
• Cells are arranged loosely with different colors, form a irregular cluster • Composed of various types of cells |

 |  |
CMCs (left) • Cells are alive without aging after long term subculture | DDCs (right) • Cells are aging or dead after long term subculture |

| 
|
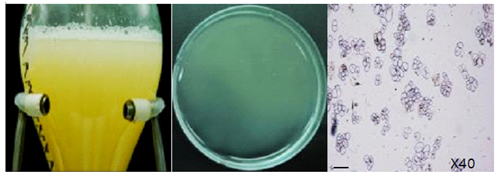
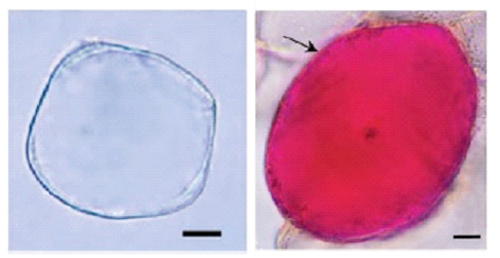
CMCs (left) • Cells are suspended within small cell cluster | DDCs (right)
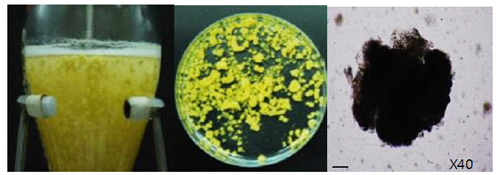
• Cells are highly aggregated and form different sizes of clusters. |

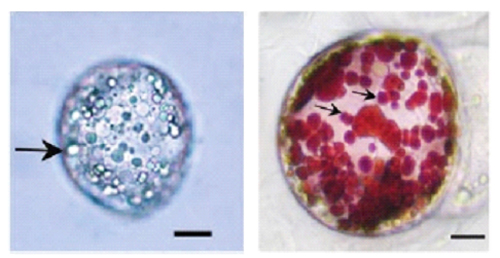
|  |
CMCs (left) • Numerous small vacuoles in the cell | DDCs (right)
• Single huge vacuoles in the cell |

| 
|
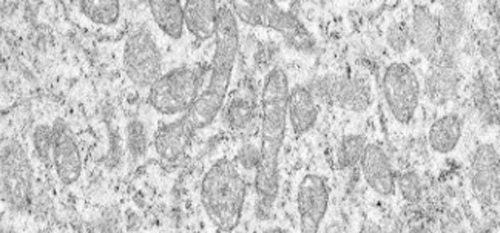
CMCs (left) • Numerous, active and diverse shapes of mitochondria in the cell |
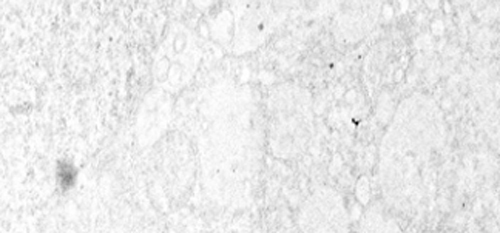
DDCs (right) • A few mitochondria in the cell |

 |  |
CMCs (left) • Faster decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into oxygen due to strong anti-oxidants in CMCs |
DDCs (right) • Slower decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into oxygen due to weaker anti-oxidants in DDCs |

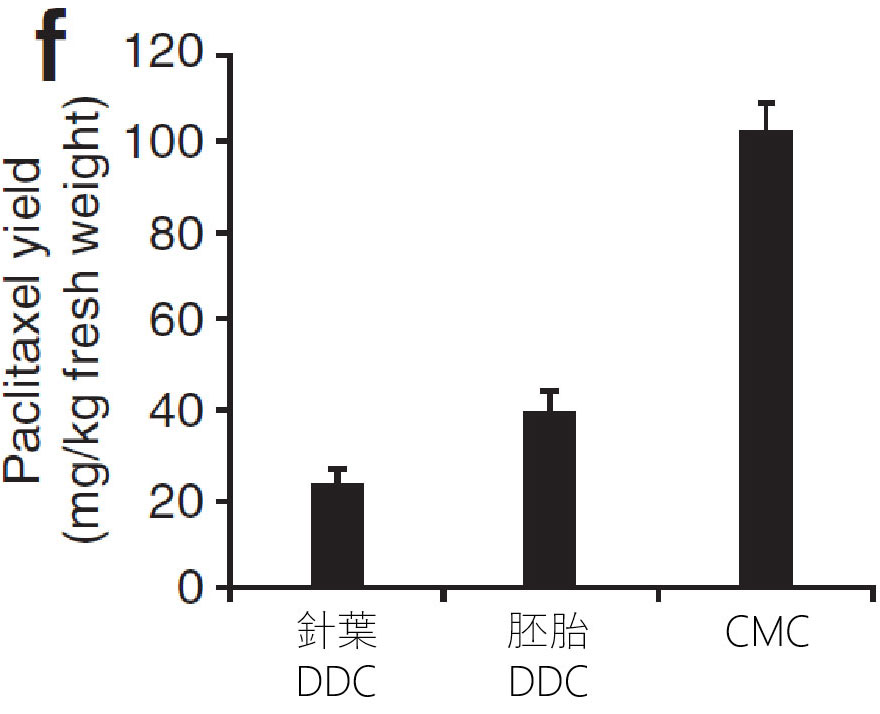
|
Needle DDCs (left) • DDCs from the yew tree leave have lower paclitaxel yield than CMCs |
Embryo DDCs (middle) • DDCs from the yew tree embryo have lower paclitaxel yield than CMCs |
CMCs (right) • Highest paclitaxel yield
|

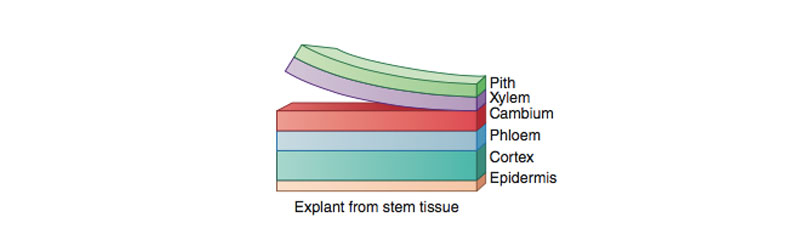
| 
|
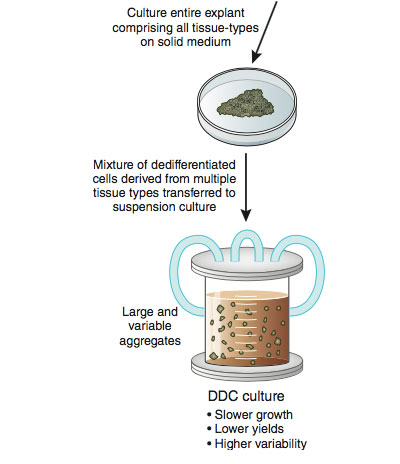
| 
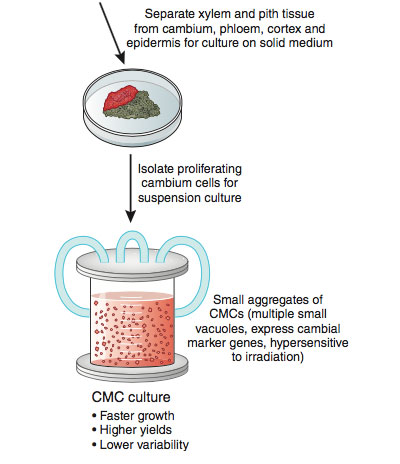
| 
|
| Callus (DDC) | Plant Stem Cell (CMC) |
| Cell composition | Heterogeneous cell types | Homogeneous cell type |
| Genetic variations | Yes | No |
| Vacuoles | Single large vacuole | Numerous and small |
| Cell aggregation | Big cell clusters | Single or small cell clusters |
| Shear stress damage | Sensitive | Resistance |
| Cell viability | Low | High |
| Growth rate | Slow and unstable | Fast and stable |
| NP biosynthesis | Decrease or loss | Stable and high |